In today’s hyper-connected society, where devices communicate across continents in milliseconds, digital privacy has become one of the most critical issues for individuals, businesses, and governments alike. As data is collected from virtually every online interaction, understanding how to protect this data—and knowing who can access it—has grown increasingly complex. This blog explores the challenges of digital privacy in our connected world, key concerns for individuals and businesses, and best practices to safeguard personal information.
Understanding Digital Privacy in a Connected World
Online protection of individual and organizational information falls under the category of digital privacy which includes multiple practices. The present interconnected world relies on continuous data exchange which occurs through mobile phones alongside social networks and wearable technology as well as intelligent devices. Data privacy problems shifted with technological evolution to include organization policy regarding information use as well as surveillance and data breaches and control of data possessions.
Modern digital privacy encounters two main problems during this era.
Data Collection and Surveillance
Almost every application and smart technology and website tracks data from users without proper disclosure regarding the scope of information collection and sharing capabilities. Private organizations together with state authorities possess the capability to observe digital activity that gives them potential access to private user information. The extensive monitoring practices threaten individual privacy by giving rise to worries about privacy invasion along with improper data handling.
Data Breaches and Cybersecurity Threats
Governments and private corporations track millions of users through data breaches which result in fiscal damage and identity theft and unfavorable business reputation. Digital criminal elements seek sensitive information such as financial data and healthcare records by employing vulnerabilities in systems to steal this data which they afterward sell on the black market.
The Complexity of Privacy Policies
Internet users encounter numerous privacy policies daily yet almost all policies include complex legal texts that run beyond average reading times. Users fail to understand the full scope of data sharing under these lengthy policies because the policies maintain high complexities.
Data Ownership and Control
Data sharing results in high challenges to control or retrieval of information particularly when stored throughout several servers and locations. Users who share data through cloud storage agreements surrender their personal data ownership to third parties who might exploit that data for unexpected uses.
Are you intrigued by the possibilities of AI? Let’s chat! We’d love to answer your questions and show you how AI can transform your industry. Contact Us
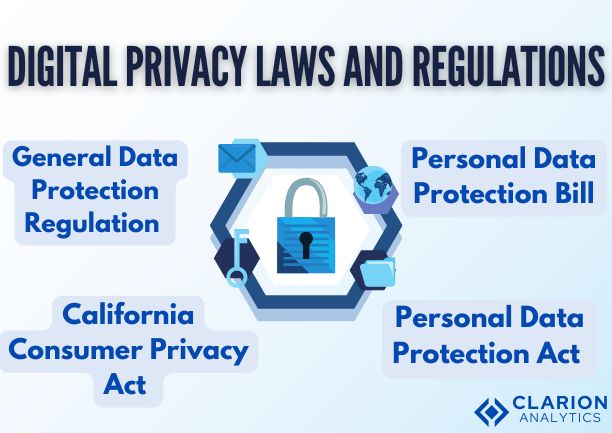
Digital Privacy Laws and Regulations
Different nations have implemented strict privacy regulations to protect personal data because privacy concerns have intensified. There exist three key privacy regulations among others:
The GDPR operating throughout European territories enables EU citizens to exercise full control of their personal information while establishing rights and procedures for accessing correcting or deleting such data at the hands of businesses.
California Consumer Privacy Act (CCPA) extends privacy protections to California residents by making enterprises reveal their data collection practices while giving users a right to refuse data trade operations.
The Personal Data Protection Bill (PDPB) gives ownership rights to data while imposing strict rules for businesses that handle data of Indian residents.
The Personal Data Protection Act (PDPA) of Singapore enforces rules about obtaining consent from users along with disclosing data usage and maintaining personal data privacy rights.
Businesses facing challenges with compliance because these privacy laws introduce different standards between regions and countries.
Why Digital Privacy Matters for Individuals and Organizations
Trust and Transparency
A business upholds better customer trust through clear data usage disclosure. People tend to interact with organizations which demonstrate responsibility while respecting privacy standards. Companies which do not safeguard customer privacy face damages to their reputation while losing customers because of this negligence.
Businesses must establish safety measures to block unauthorized personnel from accessing personal information assets.
The handling of personal data becomes vulnerable to unauthorized access because data is obtained without consent then placed in cloud storage systems which distribute information across multiple networks. The protection of privacy for individuals safeguards them from both identity theft events and financial losses as well as additional harmful misuse of their personal data.
Enhancing Security Posture
Companies need to protect customer data carefully because this effort ensures both their security operations and meets their regulatory requirements. Privacy measures act as a protective shield that stops industries from paying costly penalties because of data breaches together with cyberattacks which simultaneously destroy sensitive data and trigger major legal ramifications.
Best Practices for Safeguarding Digital Privacy
Strong passwords together with MFA authentication should be used as security measures.
The quality of passwords continues as a leading safety measure that blocks unauthorized entry attempts. The combination of complex passwords through implementation of MFA ensures added security because it demands multi-step verification to authorize access.
Limit Data Collection and Retention
Companies need to gather only necessary operational data while keeping all storage periods minimal. The reduced data breach risk along with standards compliance outcomes become achievable through these measures.
Educate Employees and Users
The organization’s employees gain the ability to detect security threats and maintain responsible data handling by receiving consistent training about data privacy methods and cybersecurity standards. People who understand privacy hazards can protect their online existence by implementing VPNs (Virtual Private Networks) while keeping their activities secure.
Stay Compliant with Privacy Laws
Organizations must uphold privacy laws for avoiding legal sanctions. Parts of business should monitor new privacy regulations by building policies that follow present-day requirements. The protection of data can be achieved by employing data encryption paired with secure access controls while performing regular audits which both support compliance maintenance.
Utilize Privacy-Centric Technologies
Users who implement privacy-centric tools consisting of privacy-focused browsers and ad blockers and secure messaging programs gain improved privacy benefits. Businesses can increase their privacy measures through the adoption of encrypted databases and secure cloud storage solutions and other privacy-centric technologies.

The Future of Digital Privacy in a Connected World
Technological progress will give rise to increased importance of digital privacy protection. Artificial intelligence together with Internet of Things (IoT) technologies create fresh data privacy obstacles by giving numerous devices the ability to accumulate and process massive amounts of data. .easing privacy concerns demands continuous investments in security solutions and user training programs and regulatory standards. Business success beyond data protection and transparent data handling yields better trust-building opportunities with their customer base.
Conclusion
Digital privacy exists beyond being a personal matter since it demands unified responsibility in the era of connectedness. Strong privacy practices combined with transparent systems enable businesses and individuals to handle the challenges of digital privacy while decreasing risks that come from data dependency. The protection of digital privacy together with establishment of a safe connected world demands practicing best practices and complying with regulations alongside responsible technology use from everyone.
Also Read:
In an era where Digital Privacy is a top priority, organizations must strengthen their AI and software ecosystems through Securing Deep Learning API: Best Practices and Challenges and Node.js Security: Best Practices for a Robust Production Environment, ensuring robust protection at both the model and infrastructure levels. Secure deployment strategies discussed in RESTful APIs – Optimizing Deep Learning Model Deployment further reinforce data integrity across connected systems. Transparency also plays a vital role, as highlighted in The Power of Explainable AI (XAI) in Deep Learning: Demystifying Decision-Making Processes, helping build trust in AI-driven decisions. To reduce operational and reputational risks, Mastering Mitigation of LLM Hallucination: Critical Risks and Proven Prevention Strategies addresses reliability concerns, while Digital Transformation and ESG: 101 connects privacy, governance, and responsible innovation within broader sustainability goals.
Are you intrigued by the possibilities of AI? Let’s chat! We’d love to answer your questions and show you how AI can transform your industry. Contact Us
