Introduction
As of right now, agentic AI, or AI systems that are made to act on their own, are typically a combination of LLMs and tools that are created in a goal-oriented manner to accomplish a specific task.
Agentic AI is a crucial innovation in a time when AI integration is quickly changing industries. This is because it meets the growing need for AI systems that can function in dynamic and unpredictable environments, like supply chain management, disaster response, and individualized education.
Readers will have a thorough understanding of agentic AI and its revolutionary potential in the contemporary world by the end of this blog.
What is Agentic AI?
Artificial intelligence systems that are made to act independently, make choices, and accomplish particular objectives without continual human guidance are referred to as agentic AI.
Agentic systems are more autonomous than reactive and limited-memory AI. They are able to pursue objectives on their own, learn from experiences, and adjust to new surroundings. For example, without human assistance, an agentic AI running a smart factory can troubleshoot problems, optimize production, and recommend upgrades.
Three distinguishing characteristics of agentic AI are what make it so magical:
Independence: Agentic AI excels in this situation. A babysitter is not required. It takes over as soon as you give it a goal. It functions without you having to hold its hand, whether you’re managing a factory floor or organizing emergency responses.
Decision-Making: What really makes agentic AI impressive is how it weighs options and makes choices. It’s like having a team of strategists in one system. It evaluates outcomes, considers risks, and picks the path that gets the job done best—all while adapting to new challenges.
Adaptability: Life isn’t static, and neither is agentic AI. If the situation changes—say, a supply chain gets disrupted or a storm derails plans—it pivots. It doesn’t just get stuck or wait for instructions; it figures out a way forward.
Are you intrigued by the possibilities of AI? Let’s chat! We’d love to answer your questions and show you how AI can transform your industry. Contact Us
Historical Evolution of Agentic AI
Decades of research, experimentation, and technological advancements have shaped the fascinating evolution that led to what is now known as agentic AI. Examining the history of artificial intelligence and the pivotal events that set the stage for the creation of fully autonomous systems is necessary to comprehend how we got here.
When pioneers like Alan Turing raised fundamental queries regarding machine intelligence in the middle of the 20th century, the idea of autonomous agents was born. The concept of intelligent agents—systems built to perceive and act toward particular goals—was first proposed by researchers in the 1950s and 1960s. These early attempts laid the groundwork for modern agentic AI, despite the fact that they were mainly theoretical due to technological constraints.
Key Milestones : A Brief Look
-
- Rule-Based Beginnings (1970s–1980s)
- Early AI, like expert systems, followed strict, pre-written rules. These were groundbreaking at the time but felt rigid and inflexible—more like calculators than problem-solvers. They couldn’t adapt or think beyond what they were told.
- The Learning Era (1980s–1990s)
- When neural networks and reinforcement learning entered the scene, AI started to learn from data and improve through trial and error. This was a game-changer, giving systems the ability to refine their strategies instead of just following instructions.
- Collaborative Intelligence (2000s)
- Enter multi-agent systems AI agents that could work together or compete. It was like giving AI the ability to play team sports or negotiate deals, paving the way for applications like autonomous vehicles and smart energy grids.
- The Deep Learning Boom (2010s–Today)
- With deep learning, AI went from useful to jaw-droppingly powerful. Systems like AlphaGo showed how agentic AI could master complex tasks independently. Add massive datasets, advanced GPUs, and transformer models, and suddenly, AI became capable of adapting, reasoning, and truly acting autonomously.
- Rule-Based Beginnings (1970s–1980s)
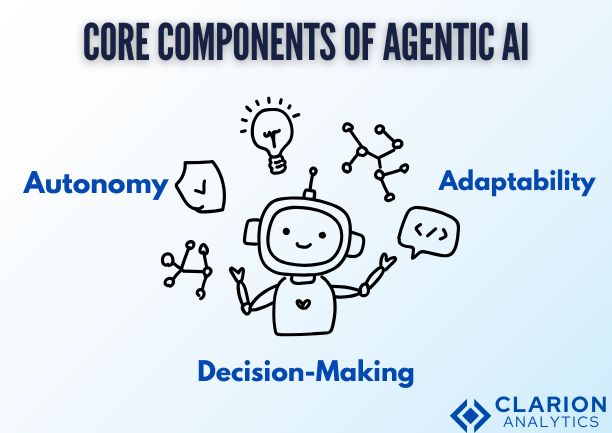
Core Components of Agentic AI
Autonomy: Agentic AI requires autonomy to function well. It can take charge and make decisions without waiting for orders once it is given a goal. Imagine a delivery drone changing course in the middle of flight to avoid inclement weather. It simply completes the task without your intervention.
Adaptability: Agentic AI remains stable in the face of change. These systems change in response to new information and shifting conditions, whether it’s a supply chain AI adapting to a factory shutdown or a smart assistant learning your changing preferences.
Making Decisions: The true magic occurs here. To make well-informed decisions, agentic AI considers a variety of factors, including probabilities, rewards, risks, and variables. For example, an autonomous car balances efficiency and safety in real time when determining when to change lanes, brake, or accelerate.
Applications of Agentic AI
Use cases from the real world in a variety of fields:
Healthcare: Envision artificial intelligence (AI) systems that actively diagnose illnesses and develop treatment plans, saving time and possibly lives.
Finance: Imagine knowledgeable advisors who foresee market patterns or identify fraud before it occurs, enhancing the intelligence and security of financial systems.
Manufacturing: Imagine robots that can instantly adjust to changes in production, ensuring that factories operate smoothly and effectively.
Transportation: Real-time route optimization and navigation by autonomous cars and traffic systems reduces traffic and increases efficiency.
Are you intrigued by the possibilities of AI? Let’s chat! We’d love to answer your questions and show you how AI can transform your industry. Contact Us
Challenges and Ethical Considerations
Technical Difficulties: There are ongoing challenges with agentic AI, such as algorithmic bias and scaling systems for complexity in the real world. It’s similar to training a genius only to discover that they don’t always read the room correctly.
Security Risks: Adversarial attacks or misuse of these systems are possible. Imagine a self-driving car being compromised—this is not a bug, it’s a serious threat.
Moral Conundrums:
Accountability: Is the user, the programmer, or the AI at fault when something goes wrong?
Oversight: It can be challenging to strike a balance between granting AI autonomy and retaining human control.
Impact on Society: Consider occupations, customs, and the changes in accountability as these systems assume greater responsibilities.
Future of Agentic AI
What Comes Next?
It is anticipated to grow even more independent, perceptive, and intelligent over the course of the next ten years. Imagine artificial intelligence (AI) systems that act and provide human-friendly justifications for their choices.
Current Research:
We can better understand why AI makes certain decisions thanks to emerging fields like Explainable AI (XAI). In the meantime, advances in neural networks will raise the bar for flexibility and judgment.
New Developments in Trends:
Anticipate deeper IoT integration, more intelligent multi-agent systems, and ethical frameworks that make AI reliable in addition to powerful.
Conclusion
Theoretically, agentic AI is becoming a reality, spurring innovation in sectors like banking, healthcare, and transportation. Although there are still obstacles to overcome, there is no denying its potential to completely transform productivity, judgment, and flexibility. Agentic systems are at the heart of AI’s promising future.
Also Read:
To fully explore the potential of Agentic AI, start with AI Agents Unleashed: Top Revolutionary Trends in Agentic AI for 2025, which highlights the latest advancements shaping autonomous systems. Gain architectural clarity through Understanding the Structure of Agentic AI: A Comprehensive Guide, and deepen your perspective with Agentic AI vs Generative AI: Crucial Differences and Their Revolutionary Impact, which explains how agent-driven systems differ from traditional generative models. For practical implementation, Autonomous Agents Accelerated: Smarter AI with the Model Context Protocol showcases orchestration frameworks powering intelligent workflows, while Unlock the Power of LangChain: A Comprehensive Guide to Building Custom Chatbots demonstrates how developers can build dynamic agents. Finally, Mastering Mitigation of LLM Hallucination: Critical Risks and Proven Prevention Strategies ensures reliability and trust when deploying Agentic AI solutions at scale.
Are you intrigued by the possibilities of AI? Let’s chat! We’d love to answer your questions and show you how AI can transform your industry. Contact Us
